Hot-dip galvanizing process
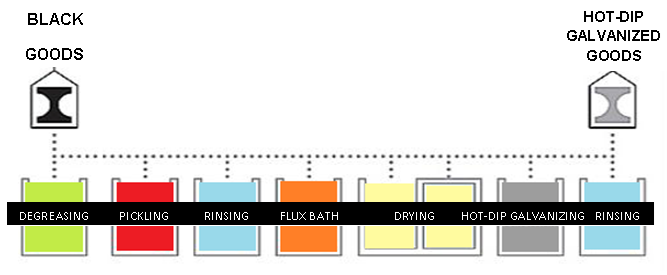
Figure 1: Technological operations in the hot-dip galvanizing process.
Hot-dip galvanizing is an anticorrosive protection by which the steel or cast iron is protected against corrosion with zinc coating. In this way we get a product that has the features of steel and the corrosion resistance of zinc.
There are two mail phases in the hot-dip galvanizing technology:
- Chemical preparation of materijal
- Dipping process.
The surface for hot-dip galvanizing shall be prepared as follows:
- Degreasing – in water solution of specific biodegradable surfactants at 40°C and slightly increased pH value. The degreasing time for the material is between 10 and 20 minutes.
- Pickling – in 4-16% solution of hydrochloric acid at room temperature. Pickling takes between 20 and 60 minutes, depending on the strength of the acid and the amount of corrosion on the material.
- Rinsing – in water at room temperature, by immersing and bringing up the material completely.
- Flux bath – in water solution of zinc and ammonia chloride, at 40°C. Performed by immersing the material into the flux bath and bringing it up.
The surface of the material prepared in this way should dry 15 to 20 minutes at 65°C and then starts the hot-dip galvanizing process by slow immersion of goods into the molten zinc at 450°C and bringing up. At this temperature an optimal intermetallic layer corrosion protection is created, when the content of zinc is increased from the center of the material towards the surface, reaching 100% at the surface.
The finished product is then cooled down, after which the inspection, additional finishing and visual check of the zinc coating thickness is performed.
The hot-dip galvanizing and the quality control are performed in accordance with standards HRN EN ISO 1461 and HRN EN ISO 14713-2.






